Docker Containers
Enabling the Docker integration
This integration must first be enabled. If you directly run on the host system and you have docker installed, it will be enabled by default. Otherwise, you'll need to mount the docker socket to the Homarr container, so Homarr can interact with the Docker service.
In Docker Compose, you can simply add this line:
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Homarr - A simple, yet powerful dashboard for your server. #
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
services:
homarr:
container_name: homarr
image: ghcr.io/homarr-labs/homarr:latest
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock # <--- add this line here!
- ./homarr/appdata:/appdata
environment:
- SECRET_ENCRYPTION_KEY=your_64_character_hex_string # <--- can be generated with `openssl rand -hex 32`
ports:
- '7575:7575'
With docker run, add this parameter: -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock.
In Windows, you'll need to adjust the slashes: -v //var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
Managing your Docker containers within Homarr
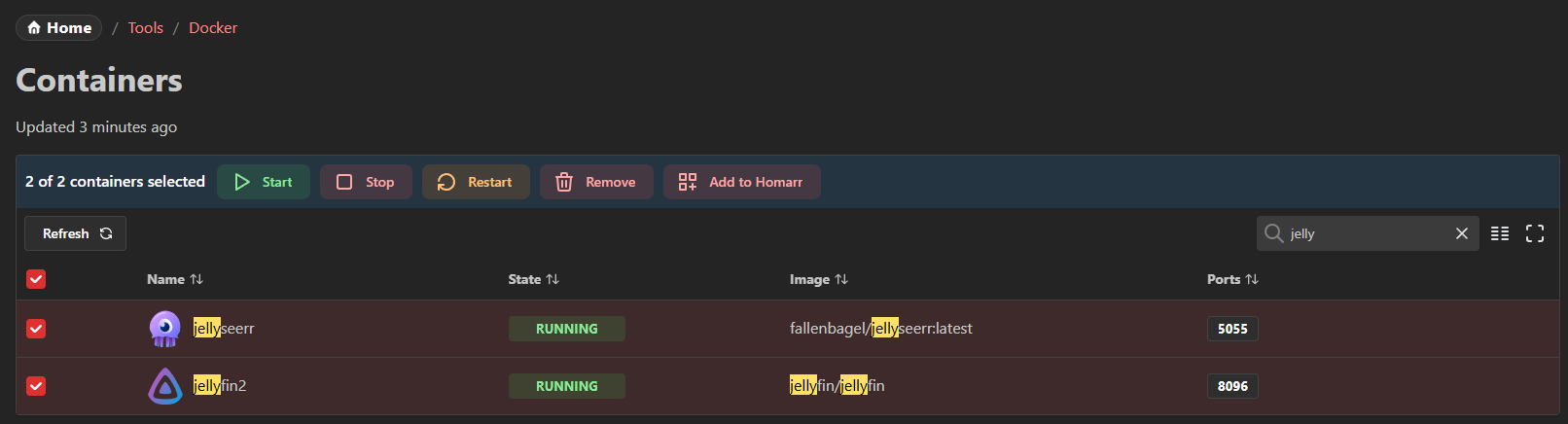
Homarr allows you to interact with Docker containers running on your system. You can restart, stop, start, refresh and remove containers. A search also allows you to search through your containers.
Additionally, if you have a lot of containers you can search and filter them by container or image name:
Add apps from containers
Homarr also lets you add apps from containers. You can simply select all containers you want to add an app for and then click the Add to Homarr button.
This will open a dialog where you can specify the web addresses for all of them:
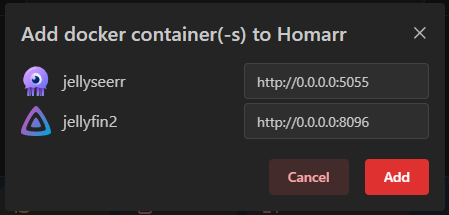
Once you've changed the web addresses, click the Add button to add the apps to Homarr.
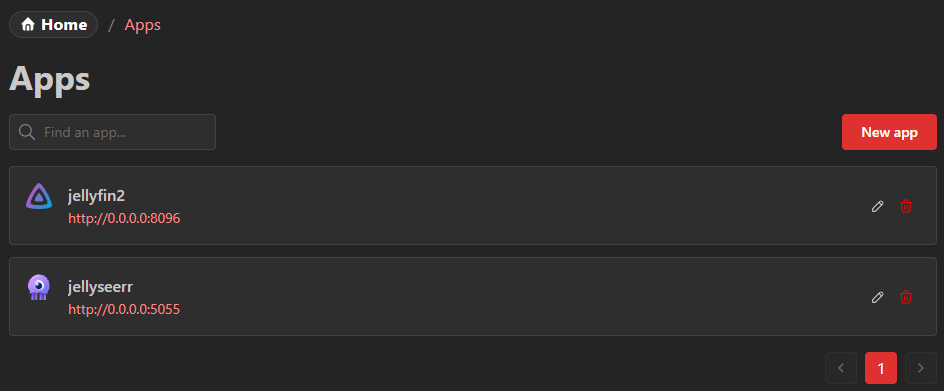
They are then available in the app list and can be used as normally added apps.
Security
Mounting docker sockets can be risky, as they permit full control over your docker service. As an example, a thread actor could abuse Homarr use the socket to start, stop or delete containers on your system.
Therefore we recommend the usage of a socket proxy, which can prohibit certain actions. A few examples include:
See documentation of the respective proxies on how to configure them. Homarr may behave in unexpected ways when you use proxies.
Permissions
Homarr needs the following permissions from the Docker API:
- Containers/Start
- Containers/Stop
- Containers/Restart
- Containers/Remove
For socket proxies, you will need these permissions:
CONTAINERS=1POST=1
Caution: POST access is security critical as it provides extensive capabilities to modify your docker environment. Please leave it disabled if you're concerned about this.
As a workaround, you can use LSIO's socket proxy and set the following:
- ALLOW_START=1
- ALLOW_STOP=1
- ALLOW_RESTARTS=1
These will work even with POST=0.
You lose the ability to remove containers, but start, stop and restarts should work just fine.
Connecting to Docker via Socket Proxies
To connect to Docker via a socket proxy, you'll need to add these two environment variables in the compose file:
DOCKER_HOSTNAMES=<name of the socket proxy container>DOCKER_PORTS=<socket proxy port, usually 2375>
Refer: https://homarr.dev/docs/advanced/environment-variables/
You will also need to add Homarr to the network of your socket proxy. You can do it like this:
- Add the network to your compose file (with appropriate changes):
networks:
socket-proxy:
name: socket-proxy # <--- change this to the name of the network as set up by the socket proxy
external: true
- Add the network to the homarr service in the compose file:
networks:
- socket-proxy
- Finally, if it is present, remove the default docker socket connection under
volumesin the homarr service.